Subsystems / Cannon / KPV
KPV
General Facts
- TYPE
Heavy machine gun - ORIGIN
 USSR
USSR - NICKNAMES
PKP (early designation for KPV)
Type 56 (Chinese production) - DESIGNED
Early 1940's - DESIGNER
Vladimirov - PRODUCTION
1944 - present - PRODUCERS
 China - state arsenals
China - state arsenals
 Russia - V.A. Degtyarev plant
Russia - V.A. Degtyarev plant
 USSR - V.A. Degtyarev plant
USSR - V.A. Degtyarev plant - QUANTITY
Unknown - UNIT COST
Unknown - CHARACTERISTICS
 Rugged and reliable
Rugged and reliable
 Very powerful for a heavy machine gun
Very powerful for a heavy machine gun
 Limited production cost
Limited production cost
 Too heavy for infantry use
Too heavy for infantry use
 Heavy recoil
Heavy recoil
 Limited range for anti-aircraft use
Limited range for anti-aircraft use
Introduction
The KPV is a powerful heavy machine gun of Soviet origin. It was developed during World War 2 for infantry use. The intended targets were infantry positions, armored vehicles and aircraft. The KPV has become one of the most ubiquitous Soviet weapons. It has been used on numerous armored vehicles, anti-aircraft gun mounts and patrol craft.
Design
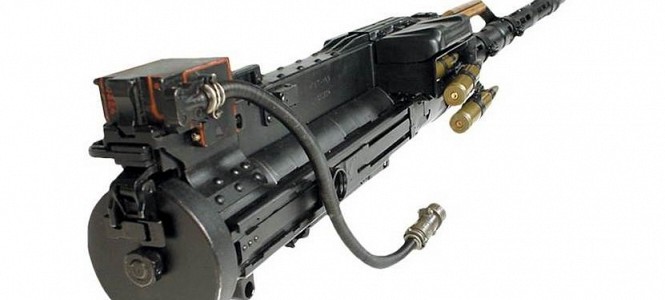
The KPV is a gas operated weapon that uses the short recoil mechanism and has a rotating bolt. It is belt fed and feeds from either left or right. A slotted shroud covers the air cooled barrels. These can be changed but are not true quick change barrels. The KPVT is a derivative for vehicle use. It has a heavier barrel jacket, shorter receiver and can be solenoid fired.
Firepower
The KPV fires the 14.5x114mm round from a 50 round belt. The cyclic rate of fire is 550 to 600 rpm. For a heavy machine gun the KPV is very powerful. It has twice as much muzzle energy as Soviet and Western 12.7mm heavy machine guns. In theory the maximum range is 3 km against ground targets and 2 km against aircraft. In practice the effective ranges are 2 km and 1.5 km respectively. Since most armored fighting vehicles are designed to withstand 14.5mm rounds over the frontal arc the KPV is no substitute for an autocannon.
Platforms
The KPV was issued on a Kharanin two wheel mount for infantry use during World War 2, but saw limited use. In post war use the KPVT saw widespread use on the ZPU series of light anti-aircraft guns that mount one, two or four KPVT. The KPVT is also used as the primary armament of many Soviet armored fighting vehicles, including the BTR-60PB, BTR-70, BTR-80 and BRDM-2. The KPVT has also been mounted on numerous patrol craft. Usually on the MTPU pedestal mount or naval derivatives of the ZPU mounts.
KPV
KPV: Original version of the KPV developed during World War 2. It is lighter than the KPVT which has a thicker barrel shroud.
KPVT: KPV modified for mounted use. It has a heavier barrel jacket, shorter receiver and is either trigger or solenoid fired.
- Specifications:
- KPVT
| Type | Heavy machine gun |
|---|---|
| Caliber | 14.5x114mm Soviet |
| Mechanism | Gas operated, short recoil mechanism with rotary bolt |
| Barrel | 1.346 m, rifled |
| Dimensions | 1.980 m long, 162 mm wide, 225 mm tall |
|---|---|
| Weight | 52.5 kg overall |
| Feeding | Single belt feed, 40 or 50 round belt |
| Rate of fire | 550 - 600 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 1.005 m/s |
|---|---|
| Recoil | ? |
| Remarks | - |